HTTP Basic Authentication
HTTP Basic Authentication provides a quick way to authenticate users of your application without setting up a dedicated "login" page. To get started, attach the auth.basic middleware to your route. The auth.basic middleware is included with the Laravel framework, so you do not need to define it:
Route::get('profile', function () {
// Only authenticated users may enter...
})->middleware('auth.basic');
auth.basic middleware will use the email column on the user record as the "username"..htaccess file:
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Authorization} ^(.+)$
RewriteRule .* - [E=HTTP_AUTHORIZATION:%{HTTP:Authorization}]
Stateless HTTP Basic Authentication
You may also use HTTP Basic Authentication without setting a user identifier cookie in the session, which is particularly useful for API authentication. To do so, define a middleware that calls the onceBasic method. If no response is returned by the onceBasic method, the request may be passed further into the application:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth;
class AuthenticateOnceWithBasicAuth
{
/**
* Handle an incoming request.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @param \Closure $next
* @return mixed
*/
public function handle($request, $next)
{
return Auth::onceBasic() ?: $next($request);
}
}
Next, register the route middleware and attach it to a route:
Route::get('api/user', function () {
// Only authenticated users may enter...
})->middleware('auth.basic.once');
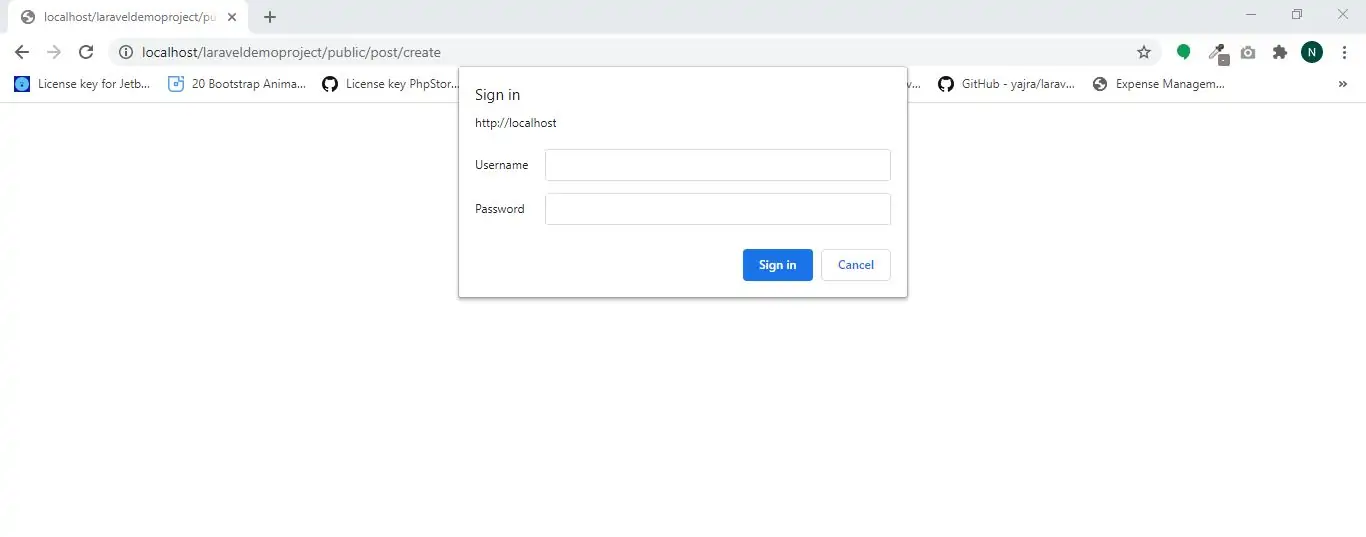
Example(1)
1.Create route in web.php file
Route::get('post/create', 'PostController@create')->middleware('auth.basic');
2.You can see by opening app\Http\Kernel.php file
<?php
namespace App\Http;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Kernel as HttpKernel;
class Kernel extends HttpKernel
{
/**
* The application's global HTTP middleware stack.
*
* These middleware are run during every request to your application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $middleware = [
\App\Http\Middleware\TrustProxies::class,
\App\Http\Middleware\CheckForMaintenanceMode::class,
\Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Middleware\ValidatePostSize::class,
\App\Http\Middleware\TrimStrings::class,
\Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Middleware\ConvertEmptyStringsToNull::class,
];
/**
* The application's route middleware groups.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $middlewareGroups = [
'web' => [
\App\Http\Middleware\EncryptCookies::class,
\Illuminate\Cookie\Middleware\AddQueuedCookiesToResponse::class,
\Illuminate\Session\Middleware\StartSession::class,
// \Illuminate\Session\Middleware\AuthenticateSession::class,
\Illuminate\View\Middleware\ShareErrorsFromSession::class,
\App\Http\Middleware\VerifyCsrfToken::class,
\Illuminate\Routing\Middleware\SubstituteBindings::class,
],
'api' => [
'throttle:60,1',
'bindings',
],
];
/**
* The application's route middleware.
*
* These middleware may be assigned to groups or used individually.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $routeMiddleware = [
.........
'auth.basic' => \Illuminate\Auth\Middleware\AuthenticateWithBasicAuth::class,
.........
];
/**
* The priority-sorted list of middleware.
*
* This forces non-global middleware to always be in the given order.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $middlewarePriority = [
.......
];
}
3.Open app\http\Middleware\AuthenticateWithBasicAuth.php which create authentication for user
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Auth\Middleware;
use Closure;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Factory as AuthFactory;
class AuthenticateWithBasicAuth
{
/**
* The guard factory instance.
*
* @var \Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Factory
*/
protected $auth;
/**
* Create a new middleware instance.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Factory $auth
* @return void
*/
public function __construct(AuthFactory $auth)
{
$this->auth = $auth;
}
/**
* Handle an incoming request.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @param \Closure $next
* @param string|null $guard
* @param string|null $field
* @return mixed
*
* @throws \Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Exception\UnauthorizedHttpException
*/
public function handle($request, Closure $next, $guard = null, $field = null)
{
$this->auth->guard($guard)->basic($field ?: 'email');
return $next($request);
}
}