Approach 1: The error_log() function can be used to send error messages to a given file. First argument to the function is the error message to be sent. Second argument tells where to send/log the error message. In this case, second argument is set to 3, used to redirect error message to a file. Third argument is used to specify the file path of the error logging file.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
<?php // php code for logging error into a given file // error message to be logged $error_message = "This is an error message!"; // path of the log file where errors need to be logged $log_file = "./my-errors.log"; // logging error message to given log file error_log($error_message, 3, $log_file); ?>
OUTPUT
[20-Dec-2018 17:32:00 UTC] This is an error message!
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
<?php
// PHP code for logging error into a given file
// error message to be logged
$error_message = "This is an error message!";
// path of the log file where errors need to be logged
$log_file = "./my-errors.log";
// setting error logging to be active
ini_set("log_errors", TRUE);
// setting the logging file in php.ini
ini_set('error_log', $log_file);
// logging the error
error_log($error_message);
?>
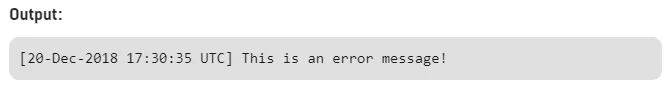
OUTPUT
[20-Dec-2018 17:30:35 UTC] This is an error message!
Similar Approach: Following lines can also be added directly to php.ini to make the configuration changes permanent for every php script that logs errors and warnings.
log_errors = on
error_log = ./errors.log
Note:: This approach is not highly reliable as compared to other approaches. Its better to use approach 1 as it gives flexibility of choosing different files for logging at same time without changing configuration of php.ini file.